
Alberts Pumpurs
In today’s digital landscape, where technology is constantly evolving, user experience (UX) is an essential factor for the success of a software product. A good user experience is key to making a product easy to use, intuitive and satisfying to the end user.
Leading companies and technological products stay ahead because they prioritize UX. They pay attention to UX aspects by making the user experience a top priority in their product design and development process. UX is an essential aspect of software products, but the importance of a specific UX aspect may vary depending on the category and purpose of the product.


Here is an example to illustrate
Imagine UX aspects as ingredients in a recipe, and depending on what kind of dish you are making, you will need different ingredients. The same applies to software products and UX aspects.
Financial software requires high security and accuracy, therefore the UX depends on the ease of use, efficiency, and overall satisfaction for the user.
On the other hand, mobile game prioritizes visual design, responsiveness, and performance to enhance user satisfaction.
An E-commerce store will prefer to focus on its visual design and navigation to improve a user’s ability to locate and purchase a product.
These examples point to one thing- Investing in UX aspects will not only improve user experience on the product but the overall revenue generated by the company.
A study by Forrester’s Research found that on every dollar invested in UX, a 70-85 % return is generated.
This highlights one of the ways a software product can be successful in today’s competitive market. With presence of many software products, you need to edge out the competition with investing in human centred design and good user experience.
A deep dive
into UX aspects
and its importance
to software products
What does UX aspect mean?
User experience (UX) aspects in design are elements that impact the user’s interaction with a software product. It refers to how a user interacts with and perceives a product or service. These aspects include elements such as ease of use, navigation, visual design, and overall satisfaction. Other important UX aspects include accessibility, performance, as well as responsiveness.
The ultimate goal of UX design is to create a positive and seamless experience for the user.
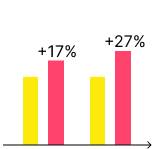
A perfect example of the impact of UX design is the redesign of the United Airlines mobile app. The redesign focused on simplifying the booking process, making it easier to use. This redesign led to a 17% increase in mobile bookings and a 27% increase in revenue for the airline.

A well-designed product that is easy to use and visually appealing is more likely to be adopted by users. On the other hand, a product that is difficult to use or unappealing is more likely to be ignored or discarded by users.
Additionally, a product that is accessible to a wide range of users, including those with disabilities, is more likely to be successful in the long term. Overall, good UX design can lead to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and conversion rates. This is why software designed with several user groups in mind does better than others.
redesign led
to a 17% increase in mobile bookings
and a 27% increase in revenue for the airline
These case studies demonstrate how good UX design has a significant impact on the success of software products. By focusing on usability and user experience, software products can improve efficiency, and ease of use, and increase customer satisfaction and revenue.
User Experience aspects in software products
Here are the UX aspect used in the study.
Ease of use. This refers to the simplicity and ease of use of a product. It includes things like clear labeling, easy-to-understand language, and logical navigation.
Navigation. The way users can move through the product or service, including the organization of content and the use of menus and buttons.
Visual design. The overall aesthetic of the product or service, including the use of colors, typography, and images.
Accessibility. This refers to how well the product can be used by people with disabilities.
Performance. The speed and responsiveness of the product or service, including load times and the ability to handle large amounts of data.
Learnability. This refers to how easy it is for users to learn how to use the product.
Efficiency. This refers to how quickly and easily users can accomplish their goals.
Memorability. This refers to how easy it is for users to remember how to use the product after they’ve used it before.
Error management. This refers to how well the product helps users recover from errors.
Satisfaction. This answers questions like- Does the user enjoy the product? did it help them complete their task or need? It helps to know how much users enjoy using the product.
Flexibility. This refers to how well the product can be used in different ways and with different types of users.
Aesthetics. Aesthetics plays an important role in how users view a product. It refers to how visually pleasing and attractive the product is.
In a study to know the UX aspect considered when a user engages in a software product.
A positive User Experience is important to the success of a software product. However, User Experience is a highly subjective concept, therefore it can be challenging to measure. Users of products are dynamic, therefore they may have different preferences, requirements, and experiences when interacting with a product. It is crucial to consider the context and objectives of the software and its target users while determining the importance of specific UX aspects in the design process.
When making a product, it’s important to think about how people will use it. By understanding what is most important to the people who will use the product, designers can make better choices. Also, it’s important to think about how culture, location, gender, or age might affect how people use the product.
How to evaluate and measure User Experience Aspects
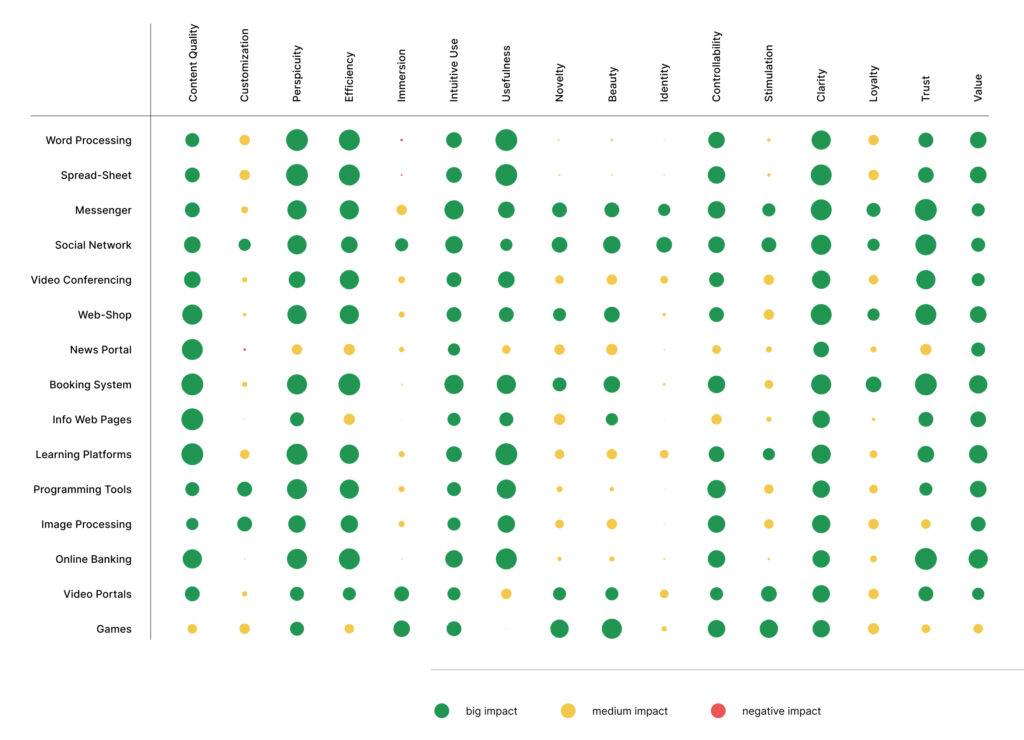
In a bid to evaluate UX aspects and its importance to software products, a study was carried out. A questionnaire containing a list of UX dimension was created on how user rate attractiveness, efficiency, control, learnability, controllability, helpfulness and originality of a product.
A selected number of participants who understand UX aspects and its description was selected for this study. The study was simple- each participant was given an excel sheet to rate 15 products categories using the important UX aspects.
Each cell could be filled
with rating from 1-7
Meaningless
This is used if the UX aspect did not make sense at all for the product category
1 – Extremely unimportant,
2 – Somewhat unimportant,
3 – Slightly unimportant,
4 – Neutral,
5 – Slightly important,
6 – Somewhat important,
7 – Extremely important.
With 16 UX aspects and 15 product categories the participants had thus to fill 240 cells, i.e. had to make 240 decisions.
This UX aspects used in this study are
The products categories tested with the above UX aspects are
Word Processing: Ms Word, MS Power Point, LaTex, Writer (Open Office)
Spreadsheet: MS Excel, Calc (Open Office)
Messenger: WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Snapchat
Social Network: Facebook, Xing, LinkedIn
Video Conferencing: Skype, Google hangout
Web Shops: Tokopedia, Bukalapak, Shopee
News Portals: CNN, BBC, Daily Telegraph
Booking Systems: Traveloka, Trivago
Info web pages: Wikipedia, Lifehacker
Learning platforms: Udemy, Udacity
Programming tools: Eclipse, Visual Studio
Image processing: Photoshop, CorelDraw, gimp
Online banking: m-BCA, mandiri mobile, jenius
Video portals: Youtube, Netflix
Games: DoTA2, Mobile Legend
| Content Quality | This shows if the software products are always actual and of good quality. |
| Customization | This indicates if a user can adapt the product to personal preferences or personal work style. |
| Perspicuity | This measures how easy it is to understand and use the product. |
| Efficiency | This measures how the product responds quickly to a user input. |
| Immersion | When I deal with the product, I forget the time. I completely sink into the interaction with the product. |
| Intuitive Usage | Can the product be used directly without any learning or the help of other people? |
| Usefulness | Is the product useful? Does using the product bring me an advantage? |
| Novelty | Is the design of the product interesting and unusual. |
| Beauty | The product is beautiful and attractive. |
| Identity | The product helps me to make contacts and to present myself positively. |
| Controllability | The product always reacts predictably and consistently to my input. I always have full control over the interaction. |
| Stimulation | This indicates how exciting and stimulating a user finds the product. |
| Clarity | The product is visually appealing and clear. |
| Loyalty | This measures how loyal a user is to a product. Even if there are other equivalent products for the same tasks, I would not change the product. |
| Trust | The data or output from the product is trustworthy. |
| Value | I find the product makes a high-quality and professional impression. |

Results and discussion
Results from the study shows that different products vary massively with UX aspects. The study looked at how important different aspects of user experience (UX) were for 15 different types of products. The study found that different products had different levels of importance for these aspects, but products that were similar in how they were used tended to have similar levels of importance for these aspects. The study also found that people had different opinions on how important these aspects were.
The study also found that some UX aspects, like intuitive usage and clarity, were seen as similar in importance across different products, while others, like content quality, varied a lot.
Multi-dimensional scaling
To visually show how similar different aspects of user experience (UX) are to each other, multidimensional scaling was further used. This was done by creating a matrix that compares the similarity of each pair of UX aspects based on how closely their importance ratings across different product categories match up. Multidimensional scaling then displays these aspects as points in a two-dimensional space, with the distance between the points reflecting how similar they are. The closer the distance, the more similar the UX aspects are.
Multi-dimensional scaling of the UX aspects.
The smaller the distance between two UX aspects is, the more similar are their importance ratings over 15 product categories
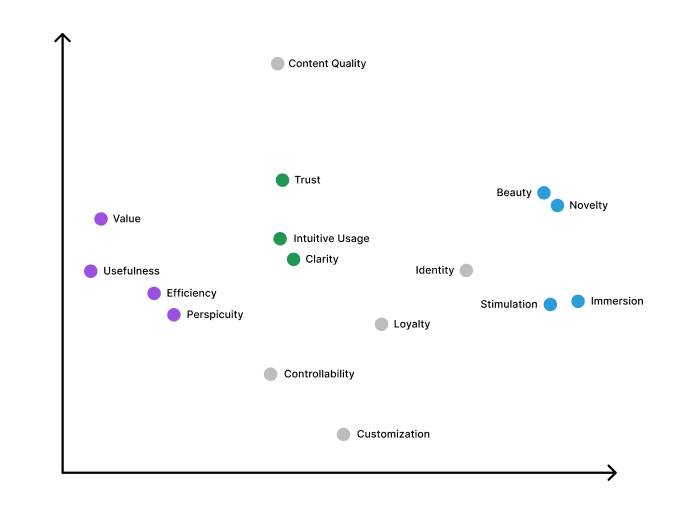
The analysis showed that there are two main groups of UX aspects: those that are related to pleasure and enjoyment (hedonic aspects), and those that are related to practical tasks (pragmatic aspects).
there are 2 main groups of ux aspects.
pleasure and enjoyment vs. usefulness and efficiency
This two main UX aspects are: those that were related to pleasure (like beauty, aesthetics and novelty) and those that were related to how well the product worked (like usefulness and efficiency). The study also used MDS to show how similar some products categories were. The study found that some groups of products, like games and video portals, were not similar to other groups, while other groups, like image processing and programming tools, were similar. While games designs needs to be visually attractive and responsiveness, a video portal product needs efficiency, intuitiveness and ease of use.


Key takeaway from this study
One of the key findings of the study was the large differences in how user perceives the UX aspect of a product. This shows the need for products and its builders to consider the needs and preferences of their target audience when designing and evaluating the user experience for a particular product.
Another important takeaway from the study was the consistent high ratings for certain UX aspects across different product categories. These include Intuitive Usage, Clarity, and Content Quality. These findings suggest that these aspects should be considered as key factors when designing and evaluating the user experience for different types of products.
The study also utilized the multidimensional scaling (MDS) visualization technique to identify the similarity and dissimilarity of the aspects and product categories. This technique helped to provide a clear and concise representation of the data, making it easier to understand and interpret the results.

In conclusion
The study provides valuable insights into the importance of different UX aspects in different product categories. It also highlights the need to consider the needs and preferences of the target audience and the importance of key factors such as Usage, Clarity, and Content Quality when designing and evaluating the user experience for different types of products. The study’s use of MDS visualization technique is also a great way to help identify the similarity and dissimilarity of the aspects and product categories for future research.
How can product builders make use of this result?
As mentioned earlier, some certain UX aspects are important to a particular product than other. Its is important that product owners and builders, factor the only UX aspect that will positively impacts their products. Users or target audience can be contacted to know their preferences.
User experience is very important to the success of a product.

How we help your product stand out irrespective of its category
All successful products consider the needs and preferences of the target audience and important UX aspects such as Usage, Clarity, and Content Quality when designing and evaluating the user experience for different types of products.
References
The Six Steps For Justifying Better UX (Forester, 2016)
Modeling aesthetic preferences: Color coordination and fuzzy sets (Shamoi, Inoue, Kawanaka, 2019)
Importance of user experience aspects for different software product categories (Santoso, 2018)

At Creative Data Studio, we help companies and product owners understand what their customers want through data insights. Our goal is to help businesses and products improve their customer relationships and engagements. We work closely with a team of creatives, web designers, developers as well as branding experts, to deliver positive results in a variety of industries.
Our unique approach combines scientific research with creativity of design and branding to help our clients achieve their product goals.
